Ciprofloxacin-Induced Renal Failure
Abstract
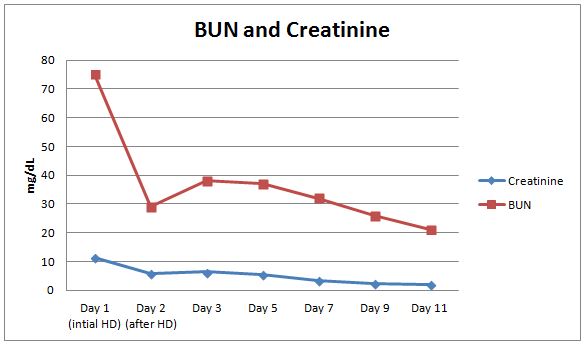
Acute renal failure (ARF) is a common diagnosis in hospitalized patients, particularly in intensive care units (ICU). Determining the cause and contributing factors associated with ARF is crucial during treatment. The etiology is complex, and several factors often contribute to its development. Medications can cause acute tubular necrosis, acute interstitial nephritis, and crystal-induced or post-obstructive nephropathy. There have been several case reports of ARF secondary to fluoroquinolones. Here we report the development of acute renal failure within a few days of initiating oral ciprofloxacin therapy and briefly describe the different types of renal failure secondary to fluoroquinolone administration. Clinical studies demonstrate that using fluoroquinolones with other potentially nephrotoxic medications requires monitoring of renal function to limit the renal toxicity with these medications. Also, the risk-benefit profile of patients requiring fluoroquinolones should be considered.Downloads